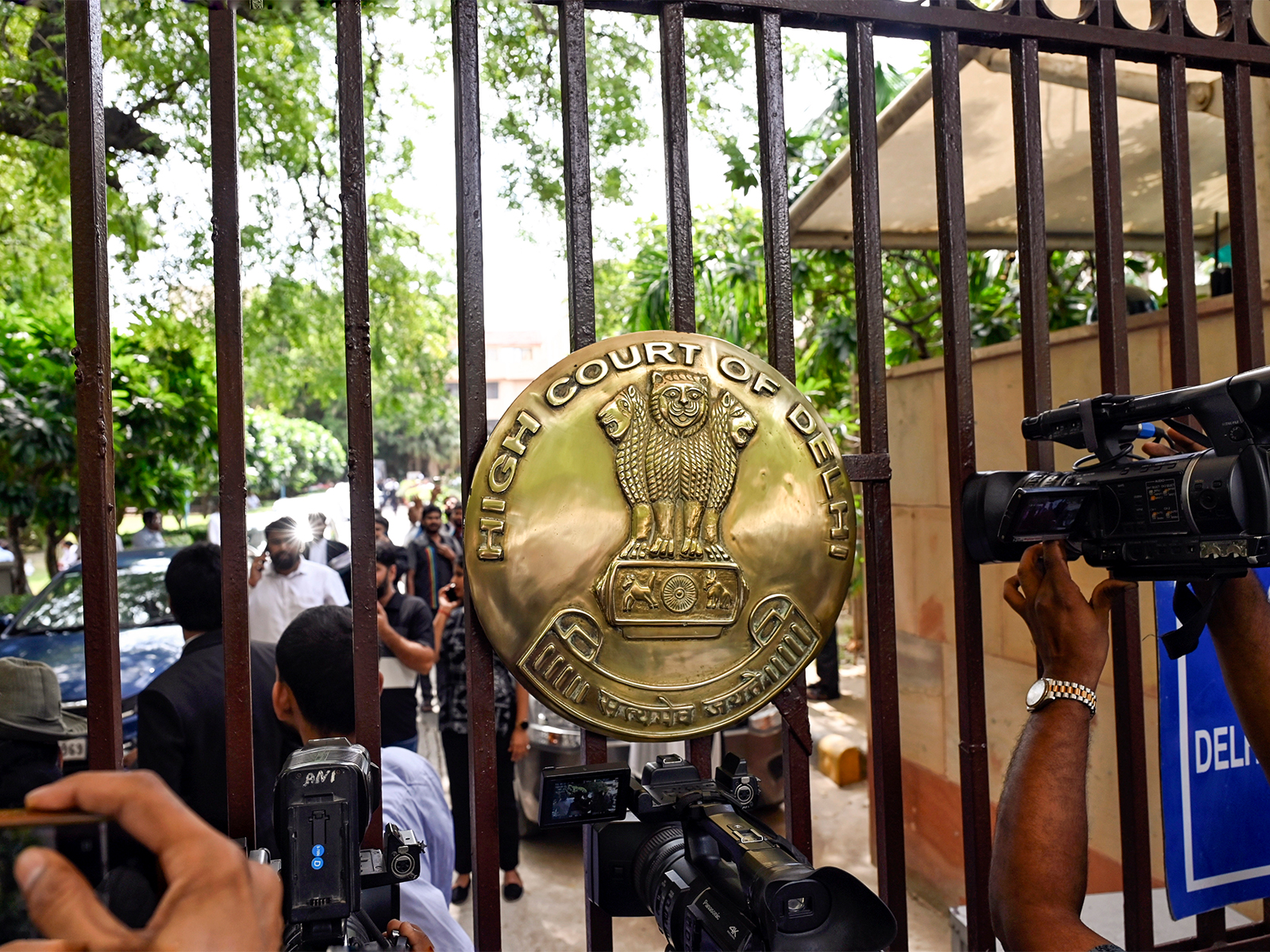New Delhi [India], September 26 (ANI): The Delhi High Court has observed that the recurring conflict between personal laws permitting child marriages and statutory provisions under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act and Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) requires urgent legislative clarity, even hinting at the need for a Uniform Civil Code (UCC).
Justice Arun Monga, while granting bail to Hamid Raza, accused of marrying a girl allegedly below 18 years, remarked that under Islamic law, a girl who has attained puberty may lawfully marry, but such a marriage simultaneously exposes the husband to prosecution under POCSO and BNS.
“Should society be criminalized for adhering to long-standing personal laws? Is it not the time to move towards a Uniform Civil Code, ensuring a single framework where personal or customary law does not override national legislation?” the Court asked.
The Court, however, clarified that it consciously refrained from expressing any conclusive opinion on the validity of the marriage, leaving the issue for trial.
Significantly, Justice Monga noted disturbing aspects of the case. The FIR was purportedly filed by the prosecutrix’s mother but bore the signature of her stepfather, who is himself facing trial for repeatedly sexually assaulting her and fathering her first child. The judge said this raised “grave doubts” about the bona fides of the FIR.
On the prosecutrix’s age, the Court highlighted inconsistencies: her date of birth ranged from 2010 to 2011 in different documents, her hospital records listed her as 17 at the time of her first delivery, while in her own affidavit she claimed to be 23. The Court held that the dispute on age could only be settled at trial.
Granting bail, the Court also found that the applicant’s arrest violated constitutional safeguards and that the trial had been inordinately delayed, infringing his right to a speedy trial.
Concluding, the Court stressed that the larger question of reconciling personal laws with child protection statutes “must soon be answered by the Legislature/Parliament” to ensure certainty and prevent misuse of criminal law. (ANI)
Disclaimer: This story is auto-generated from a syndicated feed of ANI; only the image & headline may have been reworked by News Services Division of World News Network Inc Ltd and Palghar News and Pune News and World News
HINDI, MARATHI, GUJARATI, TAMIL, TELUGU, BENGALI, KANNADA, ORIYA, PUNJABI, URDU, MALAYALAM
For more details and packages